Doms in Forearms: Why Are They Sore After Working Out?
Understanding Forearm Soreness
Forearm soreness is a common experience for many individuals, especially those who engage in regular exercise or physical activity. Whether you’re lifting weights, typing for long hours, or gripping tools, your forearms are constantly at work. This soreness can stem from various factors, including muscle strain, overuse, or poor technique. By understanding the underlying causes of forearm soreness, you can take proactive steps to prevent and manage this type of pain, ensuring a more comfortable and effective workout routine.
Pain Relief for DOMS and other Arm Pain.
There are several reasons why you might experience pain in your forearms during or after your workout. If you work out with weights, experiencing a burn as you approach fatigue, and occasionally feeling sharp pain the following day, are a matter of course. Using ice can help numb the pain receptors and reduce soft tissue swelling, providing immediate relief. However, injuries caused by resistance training are relatively common, and you should consult your physician if you have pain that is intense or persists.
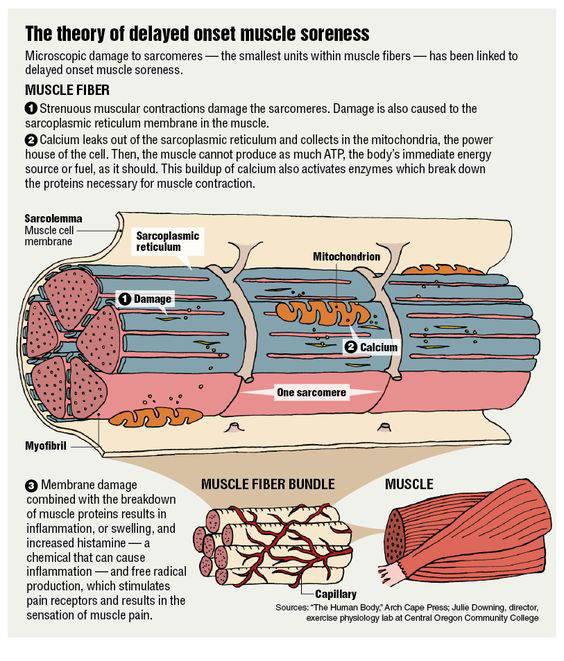
Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness and Exercise Induced Muscle Damage
Delayed onset muscle soreness, or DOMS, is the soreness that you begin to feel 12 to 48 hours after an intense workout due to exercise induced muscle damage. Soreness in your forearms, following a strenuous exercise or biceps training, is caused by micro-damage to the muscles and is not usually cause for concern. However, you should avoid training your biceps or forearms again until the DOMS has subsided. Massage and stretching exercises for the forearms can help to alleviate the pain associated with DOMS.
Causes of Forearm Soreness
Forearm soreness can be attributed to several factors, each contributing to the discomfort you might feel after an intense workout or repetitive activity:
- Muscle Strain: Overuse or repetitive strain on the muscles in the forearm can lead to soreness and pain. This is common in activities that require continuous gripping or lifting weights.
- Poor Technique: Using improper form when lifting weights or performing exercises can place unnecessary strain on the forearm muscles, leading to soreness. Ensuring correct technique is crucial to avoid this.
- Overuse: Engaging in repetitive activities, such as typing, gripping, or even certain sports, can cause strain on the forearm muscles, resulting in soreness.
- Injury: Trauma or injury to the forearm, such as strains, sprains, or tears, can cause significant soreness and pain. It’s important to differentiate between general soreness and injury-related pain to seek appropriate treatment.
Anatomy and Movement
The forearm is a complex region of the body, comprising multiple muscles, bones, and joints. It plays a crucial role in various movements, including flexion, extension, and rotation. Understanding the anatomy and movement of the forearm helps in recognizing how soreness can develop. The forearm muscles work in coordination to perform tasks, and any disruption in this harmony, whether due to overuse or poor technique, can lead to muscle soreness. By appreciating the forearm’s intricate structure, you can better understand the importance of proper care and technique during physical activities.
Muscle Tension and Tightness
Muscle tension and tightness are common culprits behind forearm soreness. When the muscles in the forearm become tense or tight, it can lead to pain and discomfort. This tension can arise from various factors, including overuse, poor technique, or injury. For instance, repetitive activities like typing or lifting weights without proper form can cause the muscles to tighten, leading to soreness. Addressing muscle tension through stretching exercises and proper warm-up routines can help alleviate this discomfort and reduce the risk of injury.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of forearm soreness can vary depending on the underlying cause. Common symptoms include:
- Pain or tenderness in the forearm
- Swelling or inflammation
- Limited range of motion
- Weakness or fatigue
Diagnosing forearm soreness typically involves a physical examination and a review of your medical history. In some cases, imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRI scans, may be ordered to rule out underlying conditions. Recognizing these symptoms early and seeking appropriate medical advice can help in managing the soreness effectively and preventing further complications.
Injury
Pain in your forearms can also signal an injury in the area. It is important to learn the difference between soreness and a legitimate injury. Common injuries of the forearms include strains, sprains and tears. If the pain you experience in your forearms during biceps curls is sudden or severe, stop training immediately and seek medical advice. Warming up your forearms with some light sets and stretches, before starting your main workout, can help you avoid injury. Consulting a healthcare professional for exercise rehabilitation can help manage and treat forearm injuries effectively.
Treatment
Consult with your doctor before undergoing treatment for Forearm muscle pain. Improving blood flow to the affected area can help reduce pain and promote healing.
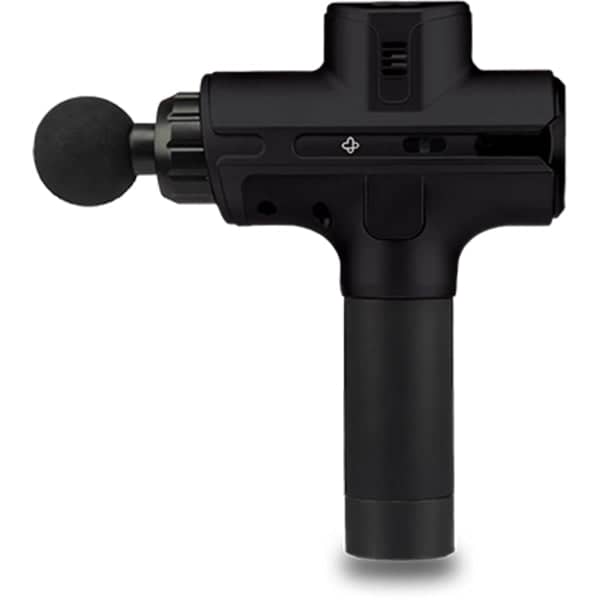
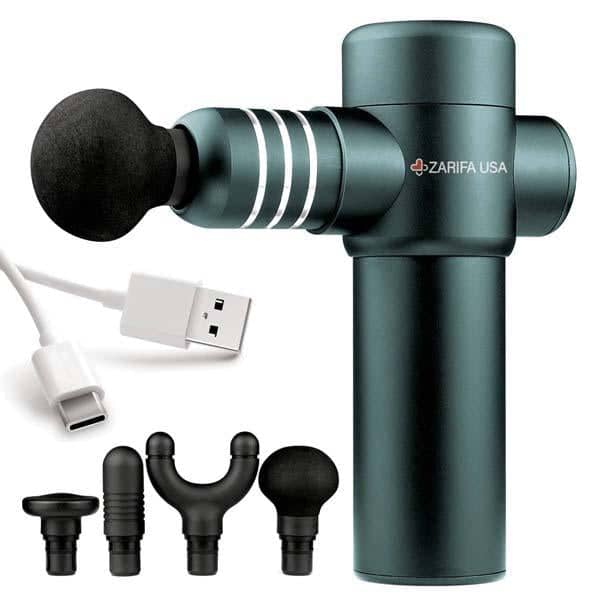
If the pain isn’t severe we recommend using our TENS and EMS Units to subside any issues you are having.
Start on a low intensity and work your way up. The Six Pack can also be used as Buttery Fly Pads on the same region.
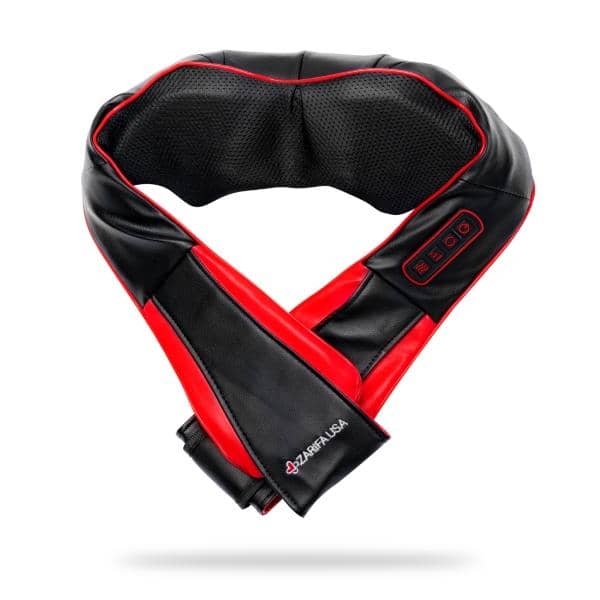
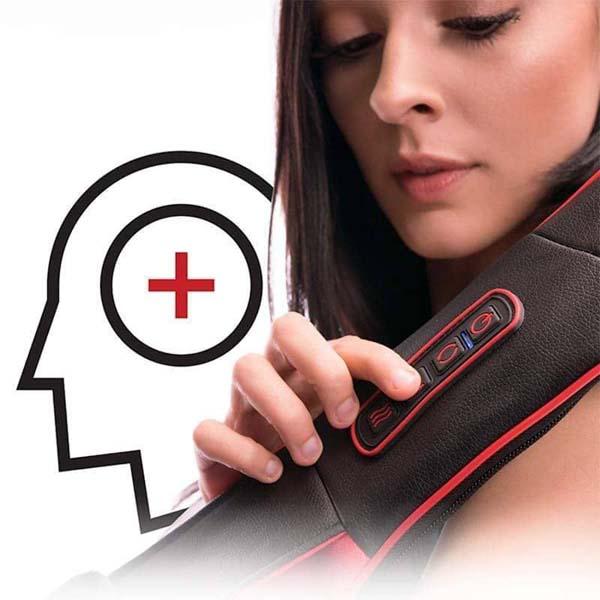
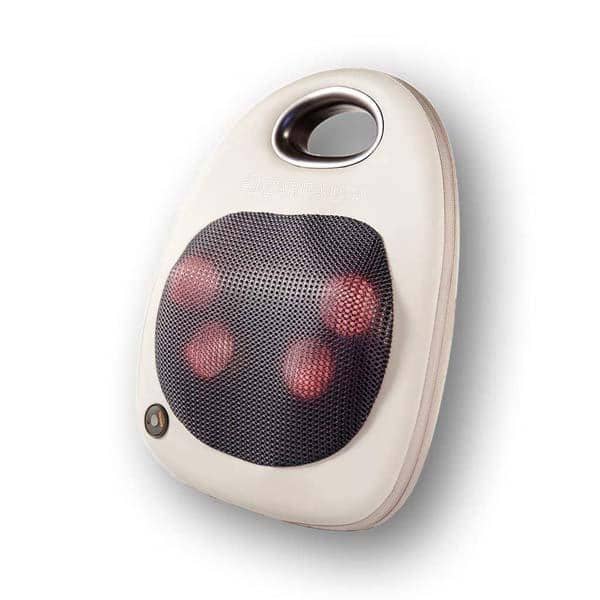
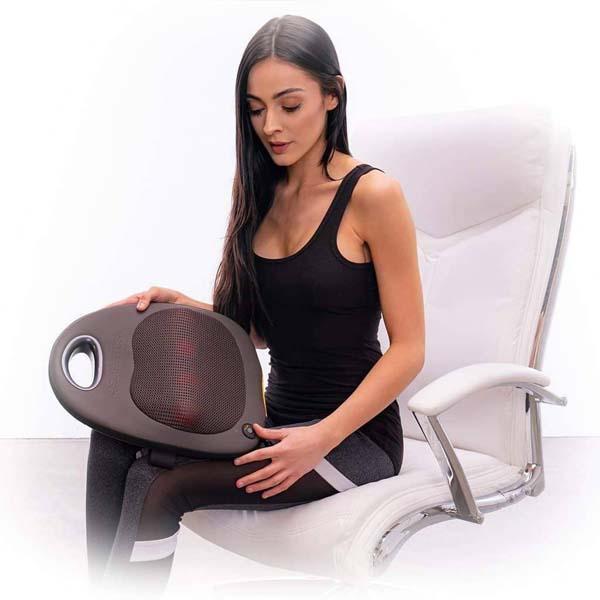
Consider our Shiatsu Pillow and Neck Massager as effective treatment options as well