You're not the only one if you have back discomfort. Back pain is one of History's most frequent health issues - not only because of sports. The daily duties of gardening and domestic labour together with an incorrect posture and ageing are typical causes of back injury. The back pain may take various forms, sometimes a strong and abrupt ache, and sometimes a persistent sluggish discomfort.
What causes back pain?
There are several probable back pain reasons. Since the back is so important, discomfort is a shockingly prevalent health issue in this area. Back discomfort is usually caused by physical damage, tight muscles, poor posture, spinal structural issues and core strength.
Urgent care to do for your lower back pain:
The degree of your pain will determine if your back discomfort requires medical care. Your main health care provider may not be accessible to assist when it hits as back problems can occur at all times. Emergency treatment can help you with pain in the back.

Anti-inflammatory medication:
In several back pain instances, the first urgent treatment involves a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicine (NSAID) such as ibuprofen (Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve). These drugs help to alleviate pain and swelling. A lot of NSAIDs may be found on the counter. In certain circumstances, your doctor may prescribe an NSAID or other anti-inflammatory prescription that is better appropriate for your specific condition.
Exercise and Strengthening:
Your provider may prescribe workouts to help treat your back pain depending on the reason and degree of the pain. Your provider can work with you to develop a safe training regimen that will assist improve your back, stomach and leg muscles. These muscles play an important function in spinal support. Easing muscles can reduce back discomfort and contribute to preventing future injuries.
Exercises for those with low discomfort in their back are beneficial. They can assist muscle repair and safeguard you from future discomfort. Your doctor may also advise reverse tension to ease muscular tension, decrease back spasms and alleviate flexibility.
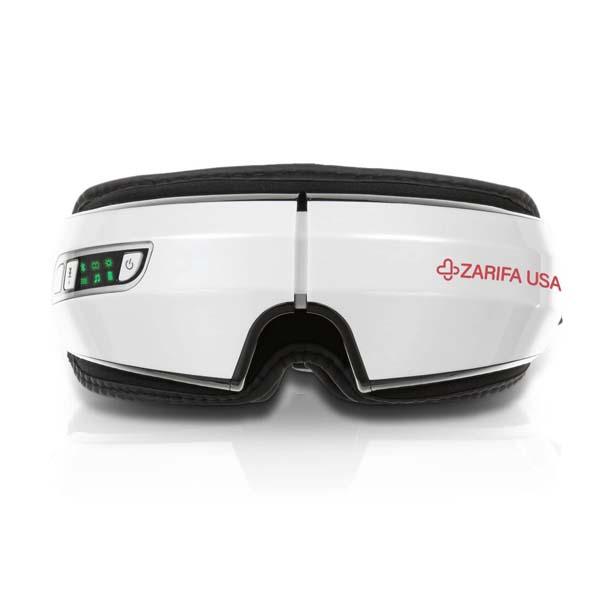
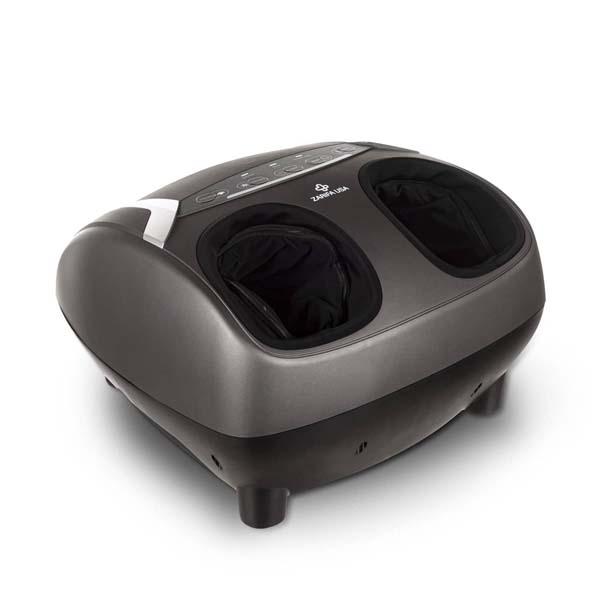
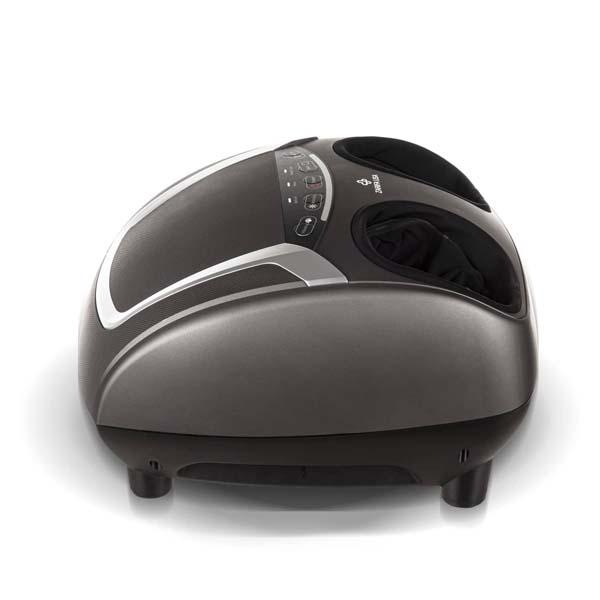
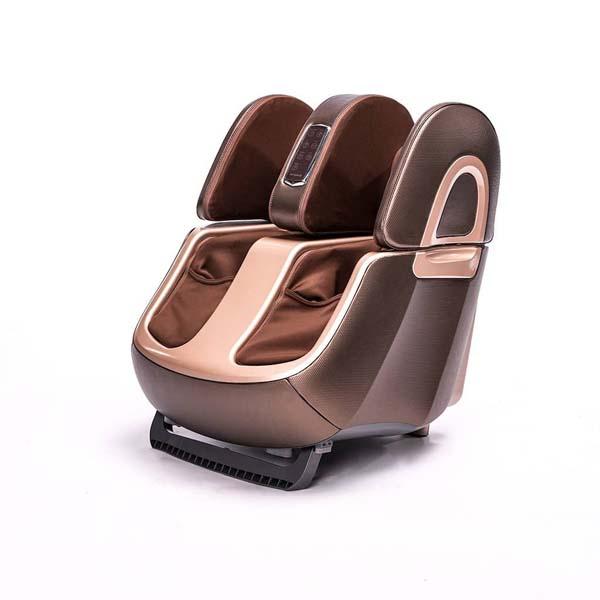
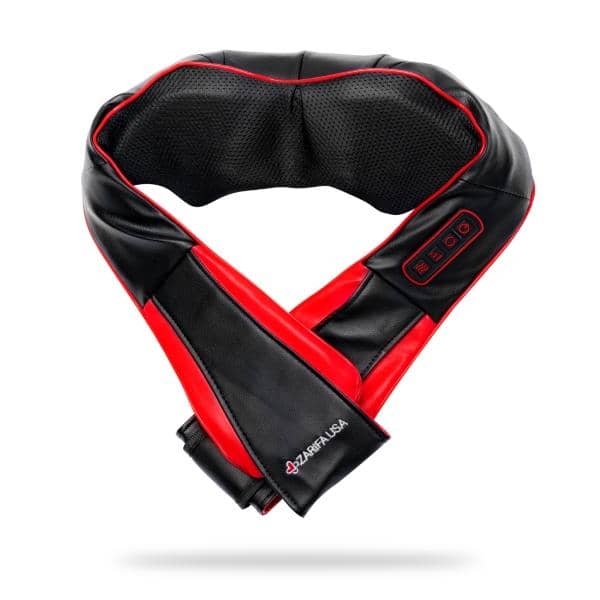
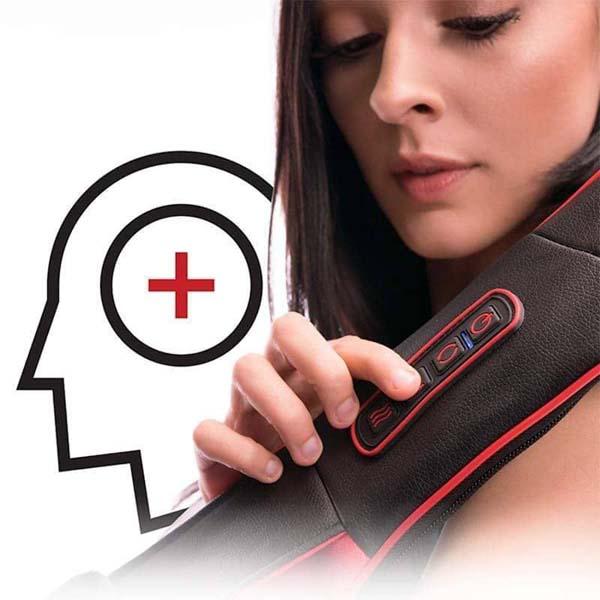
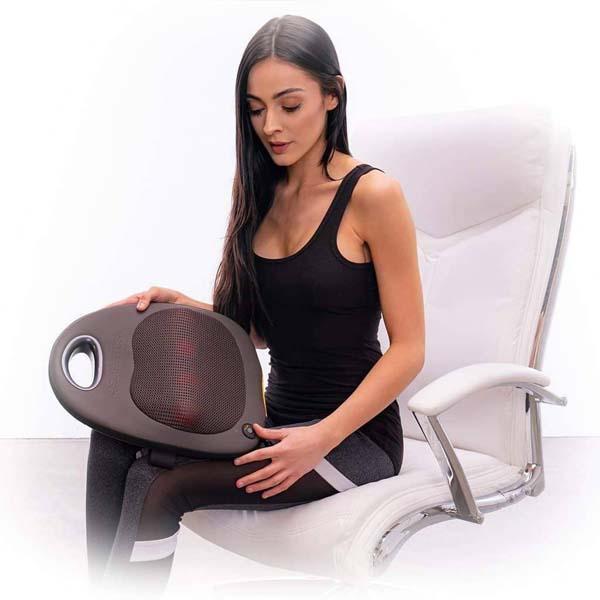
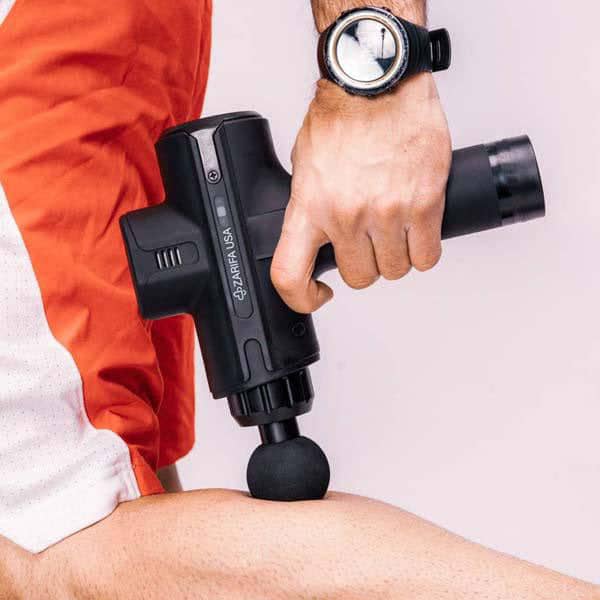
Using electric massagers:
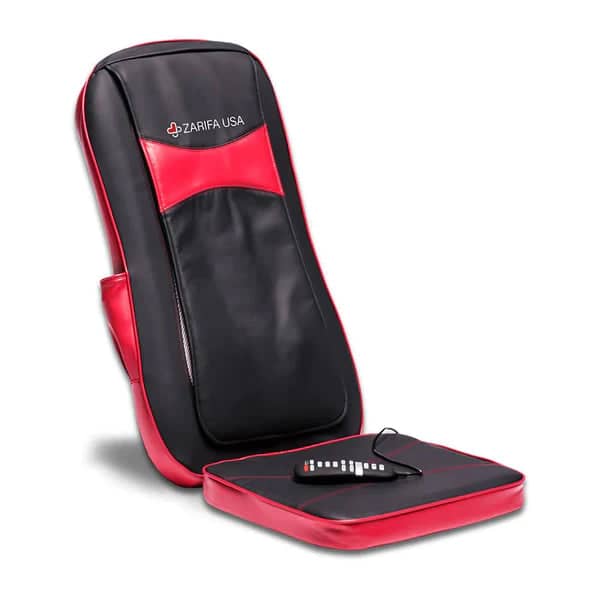
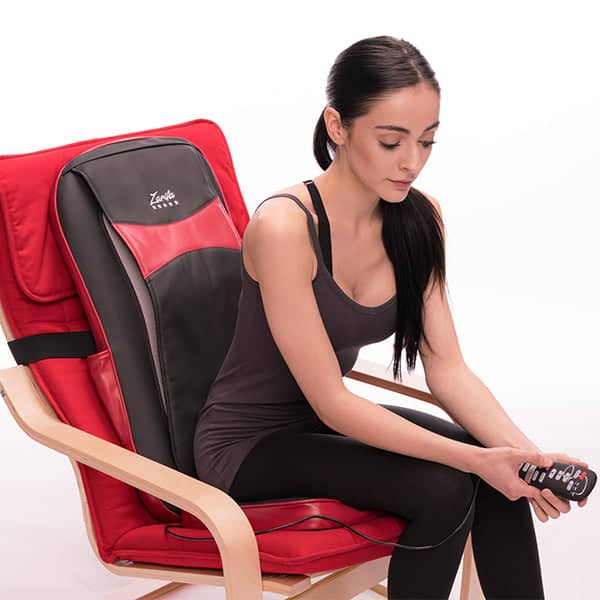
Research demonstrates that back massagers promote circulation, soothe rigid muscles and enhance your posture. It's not surprising, therefore, that you seek one!
Fortunately, back massagers can help relieve stress and stiffness in your lumbar spine. The most relieving is a massager that matches your living style and incorporates motions aimed at your pain areas such as Zarifa massager. This back massager will ease with little effort in your hard-to-reach regions. You can also focus on a particular place if there is a region in which attention truly has to be directed.
Trigger point injection:
For discomfort generated by "twists," known as trigger points, trigger point injection is recommended. This can help back discomfort by easing surrounding nerves. A physician also treats this issue with injections at trigger points (TPI).
A local anaesthetic or saline, occasionally accompanied by a corticosteroid, into the trigger site for the operation, generally takes just a few minutes. This inactivation of the trigger point relieves the discomfort.
Yoga:
There are several kinds of yoga, an extensive discipline involving the practice of certain positions, exercises and meditation. Yoga may stretch and strengthen your muscles and improve posture, however, if they exacerbate your symptoms, you may need to alter some positions.
Once you hold on, frequent stretching can successfully cure back discomfort. If you're uncertain of what to do, see your doctor for assistance in choosing on the finest back pain exercises.
Topical medication:
The feeling can be reduced by a lot of rubbing and chemicals. For example, the pain pathways in the region concerned may be desensitized by creams containing capsaicin. Research shows that topical medicines can be equally effective as oral drugs. Many of them have functioned far better than placebo. These medicines can be used as gels, creams, patches, etc.
Massaging a tight or strained muscle gently with topical medication is one of the most efficient techniques of relieving it and reducing pain.
Sleeping position:
A few days' sleep on the floor can significantly improve your back, using a pillow beneath your feet, even though it is more challenging. If you're a side-sleeper, you can relax your muscles by laying a cushion between your knees.
It might be harmful to your back to sleep on your stomach. If you can only sleep in this position, several clinics advise that you place a pillow beneath your lower belly and pelvic to reduce back stress
Epsom Salt Bath:
Epsom salt, or sulphate of magnesium, is used in the skin and in aching muscles. Soaking for around 20 minutes might help relieve back pain, particularly after activity.
You want to make sure the water is warm when you take an Epsom salt bath. Hot water can reduce swelling of muscles, whereas, cool water can cause cramping of muscles. The Arthritis Foundation advises a 92-100 F (33-38 ° C) temperature. Temperatures above 104°F (40°C), particularly if you have cardiac issues, are not suggested.
Wrapping it up!
Back pain is a frequent condition, and the older you grow, the higher it's. Indeed, at some time in their life, the majority of people deal with back discomfort. Back discomfort can become persistent for a tiny percentage.
Most lower back pain occurrences resolve themselves with therapy. In the form of prescribed medicines or injections, you will occasionally require support from your doctor. In extremely rare situations, surgery might be a possibility.
The real kicker is that you may take actions to prevent backache in those who have had back pain and who seek to avoid another spell.